Lupus Erythematosus: Symtomps and Treatment
Lupus is a chronic inflammatory disease that is caused by the immune system that mistakenly starts attacking the body's own tissues and organs. Inflammation from lupus can affect various parts of the body, for example:
- Skin
- Joints
- Corpuscle
- Lungs
- Heart
 |
| image: azarthritis.com |
The symptoms are often similar to other diseases making it difficult to diagnose. Symptoms of lupus vary. There is mild, and there are even life-threatening. This disease is not contagious, but can be dangerous and even potentially deadly. The most common symptoms are a skin rash, fatigue, pain and swelling in the joints.
Symptoms of Lupus
Symptoms of systemic lupus erythematosus (Systemic Lupus Erythematosus / SLE) is very diverse. Many patients with SLE who just feel some mild symptoms for a long time and then suddenly experienced a severe attack.
Main symptoms of SLE
Although the symptoms of SLE vary, there are three main symptoms are generally always arise, among others:
Extreme fatigue
This is the most common symptoms in SLE patients often complain. Extreme fatigue very disturbing and inhibits the activity. Many people who claim that this phenomenon is the biggest negative impact of SLE in their lives.
Doing the daily routine simple, such as housework or office routine, can make SLE very tired. Extreme tiredness persists even after the patient rested.
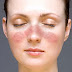
Skin rash
Which is characteristic of SLE is a rash that spreads on the nose and cheeks. This phenomenon is known as the butterfly rash (butterfly rash) because of its shape resembling butterfly wings.
Other body parts that may be covered with a rash are the hands and wrists. Rashes on the skin due to SLE may be marked permanently and is worse when exposed to sunlight due to photosensitivity reactions.
Pain in the joints
Another primary symptom of SLE is a pain. These symptoms generally appear in the joints of hands and feet of the patient. The pain may also be able to move quickly from one joint to the other joints.
SLE but generally does not cause permanent damage or defects in the joints. That is what distinguishes SLE from other diseases that also attacks the joints.
Other symptoms that might Accompanying
Each SLE patients experience symptoms differently. Some experience mild symptoms, and there were heavy.
There are a variety of other symptoms that may appear in addition to the main one. But not all of these symptoms will be experienced by patients. Many patients who have just suffered a major symptom.
Here are the other symptoms that may be experienced with SLE:
- Sores that continue to appear.
- High fever (38ºC or more).
- High blood pressure.
- Swollen lymph nodes.
- Headache.
- Hair loss.
- Dry eyes.
- Chest pain.
- Memory loss.
- Shortness of breath due to inflammation of the lungs, the impact of the heart, or anemia.
- The body stores excess fluid, causing symptoms such as swelling of the ankles
- Fingers and toes that turn white or blue when exposed to the cold or because of stress (Raynaud's phenomenon).
Treatment of Lupus
 |
| image: http://mycaresyracuse.com/ |
Systemic lupus erythematosus (systemic lupus erythematosus / SLE) can not be cured. The goal of treatment available is to reduce the level of symptoms, to prevent damage to internal organs, as well as minimizing the impact on the lives of patients with SLE.
Avoid Sun Exposure
Protecting skin from the sun is important for patients with SLE. Skin rashes experienced by patients with SLE may worsen if exposed to sunlight. Steps that can be done is:
- Wearing clothing that covers all parts of the skin.
- Wear a hat and sunglasses.
- Applying sunscreen with a high dose so that the skin is not sunburned.
However, not all people with lupus are sensitive to sunlight. There is also no need to implement the steps above.
Special treatment may not be needed by patients with SLE with mild symptoms, but they generally still require medication to manage the symptoms. Here are the drugs that may be needed by patients with SLE.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medicines
Joint or muscle pain is one of the main symptoms of SLE. Doctors may prescribe nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to reduce these symptoms.
The nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug is a painkiller that can reduce the inflammation that occurs in the body. What kind of medications are generally given physicians in patients with SLE include ibuprofen, naproxen, diclofenac, and piroxicam.
These types of drugs (especially ibuprofen) have been sold freely and be able to treat painful joints or muscles are light. But you need prescription drugs if you experience joint or muscle pain is more severe.
SLE patients also should be wary because the drug is not suitable if they are being or have had gastric disorders, kidney, or liver. These medicines also may not be suitable for people with asthma.
Also, children under 16 years of age should not take aspirin. Again, talk to your doctor to find a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug that is suitable for you.
Consumption of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or long-term high doses can cause bleeding inside because of damage to the stomach wall. Therefore, doctors will monitor the condition of patients with SLE who must consume it for long term carefully. If complications do occur, the doctor will recommend other options.
Corticosteroids
Corticosteroids can reduce inflammation quickly and efficiently. These drugs are usually given by a doctor if SLE patients were experiencing severe symptoms or attacks.
To control symptoms and attacks, the initial stages of this medication may be a massive dose. Then the dosage is reduced gradually as the condition of the patient improved.
Corticosteroids are always given the lowest effective dose. High doses and long-term consumption of these drugs can cause side effects that include bone thinning, thinning of the skin, weight gain, and increased high blood pressure.
How to minimize the side effects of steroids is to adjust the dose of steroids with disease activity while controlling it actually. As long as you follow the recipe and supervised by a doctor, corticosteroids include drugs that are safe to use
hydroxychloroquine
Besides once used to treat malaria, the drug is also useful for treating some of the significant symptoms of SLE. Among them:
- Joint and muscle pain
- Fatigue
- Skin rash
Specialist doctors generally encourage the consumption of this drug for long-term for people with SLE. The aim is to:
- Prevent a severe attack.
- Controlling symptoms.
- Prevent the development of serious complications.
The effectiveness of regular hydroxychloroquine will be felt with SLE after taking over 1.5-3 months.
But all drugs have side effects remain, including hydroxychloroquine. Among these are indigestion, diarrhea, headache, and rash.
These drugs also have side effects more serious, but very rare. For example, it is estimated there is a risk of 1: 2000 in SLE patients taking these drugs may experience eye damage. Because it is so rare, general eye exams are not required for all lupus patients who take this medication.
Immediately consult your doctor if you experience vision problems for taking hydroxychloroquine.
Immunosuppressant Medicines
The workings of this medicine are to suppress the immune system performance. There are several types of immunosuppressants are usually given by prescription, namely azathioprine, mycophenolate mofetil and cyclophosphamide.
Immunosuppressant will relieve the symptoms of SLE to limit damage to parts of a healthy body from the attacks of the immune system. The drug is also sometimes given together with corticosteroids. If combined, they can relieve the symptoms of SLE more efficiently. The use of immunosuppressant was also likely to reduce the dose of corticosteroids needed patient.
Immunosuppressants including drugs that are very hard and can cause the following side effects:
- Gag.
- Loss of appetite.
- Swelling of the gums.
- Diarrhea.
- Convulsions.
- Easy bruising or bleeding.
- Breakouts.
- Headache.
- Weight gain.
- Excessive hair growth.
Therefore, this drug is usually administered by prescription only for SLE patients who experience severe symptoms or attacks. Immediately consult a doctor if any side effect that was more disturbing than the benefits. Your dose may need to be adjusted.
Each type of immunosuppressant cause side effects vary. For example, mycophenolate and cyclophosphamide can cause birth defects. Therefore, patients with SLE women using either of these medications and are sexually active are encouraged to use contraception is guaranteed potency.
For patients with SLE women who intend to have children, you are advised to choose other drugs (e.g., azathioprine). You are also advised to first consulted the specialist.
Pregnancy should be planned when you reduced SLE symptoms (remission). Careful monitoring of specialists and obstetricians during pregnancy takes place also very important.
The risk of infection increases with the performance of the immune system is suppressed. Contact your doctor immediately if you experience symptoms of infection since you may need immediate treatment to prevent serious complications.
Symptoms of infection are sometimes similar to lupus attacks and includes:
- Coughing accompanied by phlegm or panting.
- High fever (38ºC or more).
- That feels a burning sensation during urination.
- Blood urine (hematuria).
Avoid contact with people who are experiencing an infection as anything or even if you already have immunity against infection, such as chickenpox or measles. Transmission may still occur due to the performance of your immune system is on the decline because of pressure by the immunosuppressant drugs.
Immunosuppressant also can cause liver damage. Therefore, you need a medical examination and regular blood tests while using immunosuppressants.
Rituximab
If other drugs are not effective for patients with SLE, the doctor will recommend rituximab. These drugs included a new type and was originally developed to treat certain blood cancers, such as lymphoma. But rituximab proved useful in dealing with autoimmune diseases such as SLE and rheumatoid arthritis.
How it works is by targeting rituximab and kill cells B. These are the cells that produce antibodies that trigger the symptoms of SLE. These drugs will be put through the IV that will last for several hours. During the treatment process is underway, your condition will be monitored carefully.
Common side effects of rituximab include dizziness, vomiting, and flu-like symptoms (e.g., chills and high fever during treatment). Other side effects may occur (although rarely) are allergic reactions. These reactions usually occur during treatment or shortly after that.