Hepatitis C: Symtomps, Diagnosis, Treatment and Prevention
 |
| image: healthline.com |
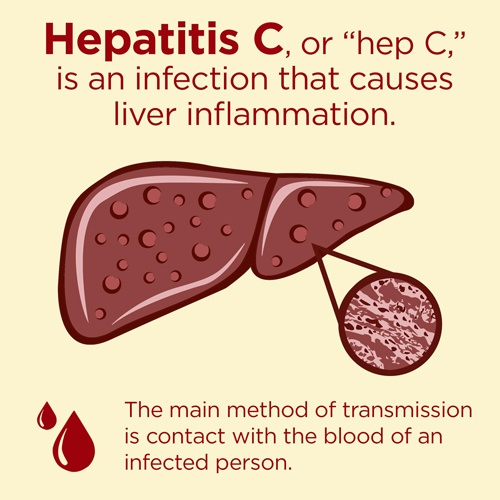
Hepatitis C is one of the diseases that can attack the liver. The disease caused by this virus can trigger the infection and inflammation of the liver.
According to the WHO, the number of hepatitis C sufferers in the world reached 130-150 million people and caused the death of around 350-500 thousand of its victims. While in Southeast Asia alone, the number of patients who died of complications of cirrhosis and cancer of the liver due to hepatitis C was recorded to reach 120,000 inhabitants each year. Indonesia is one of the countries with the highest rate of hepatitis C cases in Southeast Asia.
Hepatitis C generally do not show symptoms in the early stages. Therefore, about 75 percent of hepatitis C sufferers don't realize that he's been contracted until finally experiencing liver damage years later.
Although there are symptoms of hepatitis C that appears, indications are similar to other diseases so difficult to realize. Some include always feeling tired, achy, and no appetite.
Symptoms of Hepatitis C
The incubation period (the time since the virus first entered until symptoms appear) for hepatitis C is two weeks to six months.
Infection in the first six months is known as acute hepatitis C. Although there are symptoms of hepatitis C that appears, indications are similar to other diseases so difficult to realize.
Only about 25 percent of patients with acute hepatitis C who have symptoms. Some indications include:
- Fatigue.
- Muscle and joint pains.
- Fever.
- No appetite.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Stomach ache.
- Jaundice (experienced by approximately 20 percent of patients).
The immune system of patients with acute hepatitis C sometimes able to kill the virus without special treatment so that the patient will recover. It occurs in about 25 percent of sufferers.
While 75 percent of the rest will keep the virus hepatitis C for a long time. This is called chronic hepatitis C.
The symptoms of chronic hepatitis C are very diverse and vary depending on each patient. Some experience mild symptoms, and there were heavy. In addition to symptoms similar to acute hepatitis C, the following are other indications commonly experienced by patients.
- Always feeling tired.
- Headache.
- Muscle and joint pains.
- Indigestion.
- Difficulty concentrating or remembering things.
- Mood changes.
- Depression.
- Itching of the skin.
- Right upper abdomen (the location of the liver) hurt.
- Dark urine.
- Gray-colored stools.
Immediately consult a doctor if you experience the symptoms above. The diagnosis as early as possible will reduce the risk of complications of hepatitis C.
Diagnosis of Hepatitis C
The earlier handled, liver damage in people with hepatitis C can be inhibited. Therefore, people who are at high risk of contracting this disease are advised to undergo hepatitis C regularly. For example, users of illegal drugs, medical workers, and people who have had blood transfusions or organ transplants.
The inspection process is done through a blood test. There are two types of blood tests are recommended for diagnosing this disease, namely:
Antibody tests. The existence of hepatitis C indicates that you have been exposed to the virus, but does not necessarily mean you are still suffering from this disease.
Tests Polymerase Chain Reaction or PCR. This test is used to check for the presence of hepatitis C virus by detecting whether the virus is still active breed in your body or not. A positive result means your body is not completely eradicate the virus and the infection has entered the stage of chronic or long-term.
If both results of the above tests show positive results, you will be advised to undergo liver function tests. This process can be done through a blood test, ultrasound, and biopsy. These tests aim to check the level of damage that occurs in the liver and other types of hepatitis C virus, hepatitis C virus genotype is divided into six types, and each have different responses to treatment measures.
Treatment of Hepatitis C
The type of treatment that will be undertaken of patients with hepatitis C depending on the degree of liver damage, as well as viral genotype diidapnya. But if positively diagnosed with hepatitis C, you may not necessarily need treatment steps.
Most acute hepatitis C can be cured without any special handling. Your doctor may recommend a blood test to monitor whether the patient's immune system successfully cleared the virus for 12 weeks. If the infection persists, your doctor will usually prescribe pegylated interferon for six months. Pegylated interferon is a synthetic protein that triggers the immune system to attack the virus.
Another case with acute hepatitis C, chronic hepatitis C patients in need of measures taken by the drugs as soon as possible. In addition to pegylated interferon, patients will also be given the antiviral drug ribavirin to inhibit the spread of hepatitis C virus in the body. But these drugs should not be taken by pregnant women because it can harm the unborn baby.
The duration of combination therapy with pegylated interferon and ribavirin depends on the genotype of the hepatitis C virus patient pathway. Genotype 1 hepatitis C virus including the types that are difficult to handle. Therefore, on the use of the drugs is for one year.
While other genotypes are generally more responsive to the combination therapy so that the duration of treatment will be shorter, ie six months. Patients with hepatitis C genotype also had a higher likelihood of cure.
During the treatment period, the patient's condition will be monitored through regular blood tests. This process is usually recommended after treatment for one and four months.
Just like other drugs, a combination of pegylated interferon and ribavirin has the potential to cause side effects. For example, loss of appetite, anemia, fever, nausea, hair loss, depression, anxiety, difficulty concentrating, and difficulty remembering things.
Almost all patients with chronic hepatitis C who live to experience more than one type of side effects. But the side effects will generally slows as the body's adaptation to the drug.
Experts later found two types of new drugs, boceprevir and telaprevir. Both are inhibitors of the enzyme (protease inhibitors). These drugs blocking the action of enzymes required by the virus to multiply.
Boceprevir and telaprevir should be combined with pegylated interferon and ribavirin. The combination of all four of these drugs is recommended as an alternative treatment for patients with hepatitis C who have never undergone any handling or unresponsive to other treatment. Patients with hepatitis C is recommended to undergo this treatment for one year.
Boceprevir and telaprevir can also cause different side effects. Boceprevir side effects include fever, nausea, loss of appetite, and insomnia. While the side effects of telaprevir can trigger anemia, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, and an itchy rash.
Please remember that if once suffered and recovered from hepatitis C, it does not mean your body has fully immune to the virus. Although already recovered, people with hepatitis C should be careful because it remains at risk for re-infected with the same disease.
Prevention of Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C can not be prevented by vaccination. But there are some ways that we can take to reduce the risk of transmission, for example, to stop or not to use drugs and avoid sharing the use of personal items that may be contaminated with blood, such as razors or toothbrushes.
Although the disease is rarely transmitted through sexual intercourse, use of safety devices such as condoms in sexual intercourse can still keep you from hepatitis C. Especially if it comes in contact with blood, such as anal sex or menstrual blood.
Prevention of the spread of hepatitis C virus is also important. People with hepatitis C can prevent transmission using:
- Clean up and cover the wound with a waterproof plaster.
- Do not become a blood donor.
- Always clean up blood spills with household cleanser.
- Don't share needles and personal items.
Patients with hepatitis C are at risk of contracting other types of hepatitis. Therefore, doctors advise them to undergo vaccination to prevent hepatitis A and B. Influenza vaccine, and pneumococcal infections are also sometimes recommended.
Tags :
disease
Subscribe by Email
Follow Updates Articles from This Blog via Email
No Comments